Jupiter 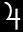
 Jupiter Facts
Jupiter Facts
| Distance from Sun: | 778,330,000 km (5.20 AU) |
| Equatorial Diameter: | 142,984 km |
| Polar Diameter: | 133,708 km |
| Mass: | 1.900e27 kg |
- Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and by far the largest
- Jupiter is more than twice as massive as all the other planets combined (318 times Earth).
- Jupiter (a.k.a. Jove; Greek Zeus) was the King of the Gods, the ruler of Olympus and the patron of the Roman state. Zeus was the son of Cronus (Saturn).
- Jupiter is the fourth brightest object in the sky (after the Sun, the Moon and Venus; at some times Mars is also brighter). It has been known since prehistoric times. Galileo's discovery, in 1610, of Jupiter's four large moons Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto (now known as the Galilean moons) was the first discovery of a center of motion not apparently centered on the Earth. It was a major point in favor of Copernicus's heliocentric theory of the motions of the planets; Galileo's outspoken support of the Copernican theory got him arrested by the Inquisition. He was forced to recant his beliefs and was imprisoned for the rest of his life.
- Jupiter was first visited by Pioneer 10 in 1973 and later by Pioneer 11, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and Ulysses. The spacecraft Galileo is currently in orbit around Jupiter and will be sending back data for at least the next two years.
- The gas planets do not have solid surfaces, their gaseous material simply gets denser with depth (the radii and diameters quoted for the planets are for levels corresponding to a pressure of 1 atmosphere). What we see when looking at these planets is the tops of clouds high in their atmospheres (slightly above the 1 atmosphere level).
- Jupiter is about 90% hydrogen and 10% helium (by numbers of atoms, 75/25% by mass) with traces of methane, water, ammonia and "rock". This is very close to the composition of the primordial Solar Nebula from which the entire solar system was formed. Saturn has a similar composition, but Uranus and Neptune have much less hydrogen and helium.
Jupiter's Satellites
Jupiter has 16 known satellites, the four large Galilean moons and 12 small ones.
- Jupiter is very gradually slowing down due to the tidal drag produced by the Galilean satellites. Also, the same tidal forces are changing the orbits of the moons, very slowly forcing them farther from Jupiter.
- Io, Europa and Ganymede are locked together by tidal forces into a 1:2:4 orbital resonance and their orbits evolve together. Callisto is almost part of this as well. In a few hundred million years, Callisto will be locked in too, orbiting at exactly twice the period of Ganymede and eight times the period of Io.
- Jupiter's satellites are named for other figures in the life of Zeus (mostly his lovers).
JUPITER'S MOONS | SATELLITE | DISTANCE(000 km) | RADIUS(km) | MASS(kg) | DISCOVERER | DATE |
| Metis | 128 | 20 | 9.56e16 | Synnott | 1979 |
| Adrastea | 129 | 10 | 1.91e16 | Jewitt | 1979 |
| Amalthea | 181 | 98 | 7.17e18 | Barnard | 1892 |
| Thebe | 222 | 50 | 7.77e17 | Synnott | 1979 |
| Io | 422 | 1815 | 8.94e22 | Galileo | 1610 |
| Europa | 671 | 1569 | 4.80e22 | Galileo | 1610 |
| Ganymede | 1070 | 2631 | 1.48e23 | Galileo | 1610 |
| Callisto | 1883 | 2400 | 1.08e23 | Galileo | 1610 |
| Leda | 11094 | 8 | 5.68e15 | Kowal | 1974 |
| Himalia | 11480 | 93 | 9.56e18 | Perrine | 1904 |
| Lysithea | 11720 | 18 | 7.77e16 | Nicholson | 1938 |
| Elara | 11737 | 38 | 7.77e17 | Perrine | 1905 |
| Ananke | 21200 | 15 | 3.82e16 | Nicholson | 1951 |
| Carme | 22600 | 20 | 9.56e16 | Nicholson | 1938 |
| Pasiphae | 23500 | 25 | 1.91e17 | Melotte | 1908 |
| Sinope | 23700 | 18 | 7.77e16 | Nicholson | 1914 |
Values for the smaller moons are approximate.

Jupiter's Rings

Distance Width Mass
Ring (km) (km) (kg)
---- -------- ----- ------
Halo 100000 22800 ?
Main 122800 6400 1e13
Gossamer 129200 850000 ?
(distance is from Jupiter's center to the ring's inner edge)
 Jupiter Facts
Jupiter Facts
